Cholera is an acute intestinal infection that affects the gastrointestinal and flowing with the development of diarrhea (sometimes acute and extremely dangerous). The causative agent, the cause of cholera, is the so -called cholera vibrio - this is the Vibrio Cholerae bacteria.
How is the infection of the cholera
The causative agent usually penetrates the body with food or water that were infected - these are the main ways of transmitting cholera. Most often, the spread of this disease is associated with the insufficient level of sanitary and epidemiological norms, as well as the fact that people themselves do not comply with the elementary rules of hygiene and eat unverified foods, drink dirty water.
The source of infection is a sick person and a bacterial carrier that releases the pathogen into the external environment.
The mechanism of infection is fecal-oral.
The infection path is the main water, secondary - alimentary and contact -household.
An increase in the incidence is noted in the summer-autumn period.
The susceptibility is universal, high. Postinfection immunity is relatively persistent.
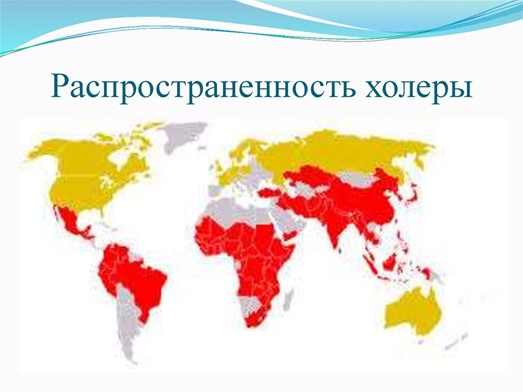
Currently, cholera epidemics caused mainly by El-Tort Vibrion arise in the tropical and subtropical countries of Asia, Africa, America, from where the pathogen can be brought to any region of the country.
The most dysfunctional ones are currently:
- on European and Asian continents: India, Laos, Indonesia, Iran, Iraq, Türkiye, Afghanistan;
- On the American continent: Bolivia, Brazil, Guatemala, Honduras, Mexico, Nicaragua, Peru, Salvador;
- On the African continent: Angola, Burundi, Ghana, Guinea, Nigeria, Somalia, Chad, Uganda, Tanzania, Sierre - Leone.
In certain countries of the CIS, cases of cholera are also recorded (for example, in Ukraine).
Symptoms of the disease
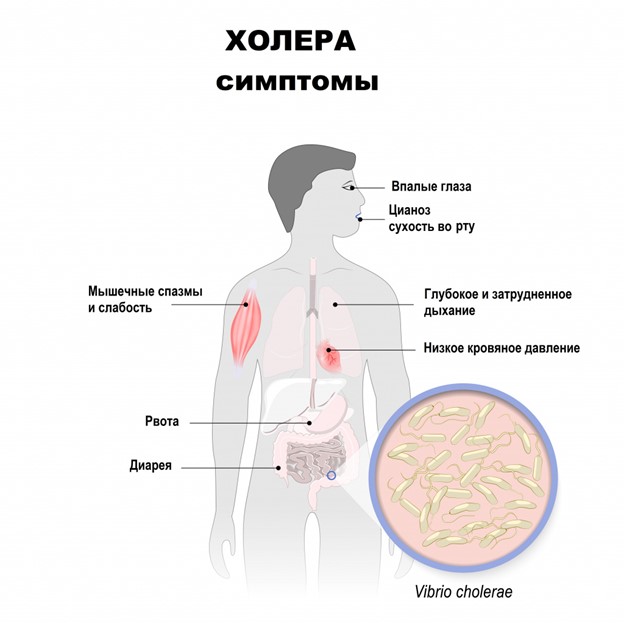
Symptoms of cholera are diverse and include the following points:
- elevated temperature (37-38ºC), which with the development of the disease can, on the contrary, decrease (to 34-35 ºC);
- chills;
- Abundant and watery diarrhea. The color of the stool is different: it can be yellow-green, and it can be brown. The bowel movements in the first hours can have a feces in nature, but quickly become colorless, watery, with abundant floating flakes, resemble a rice decoction in appearance, without the smell or with the smell of fish or grated potatoes. The frequency of defecation is from 3 to 10r/day, in more severe cases up to 30 times or is not even amenable.
- vomit. Often it occurs without urges, suddenly a fountain without previous nausea and pain in the epigastrium;
- Rumbling in the abdomen, flatulence, slight pain;
- The feeling that the stomach is full of a large amount of liquid;
- Sensation of dryness. The lips dry, you constantly want to drink, there is serious weakness. In some cases, the lips may blue;
- decrease in blood pressure, which is associated with dehydration;
- Headaches - and the pain itself is localized in the frontal part.
It is important to understand that these symptoms of cholera are not limited. If the patient does not provide timely assistance, he risks getting complications - and with them the picture is much worse.
Complications at the Hollow
It is not enough to know the symptoms and causes of cholera - it is necessary to understand how this difficult disease threatens. Here are just a few points:
- acute renal failure, disorder of various metabolic processes in the body with an unpredictable result;
- strong drop in blood pressure;
- myocardial infarction;
- Violation of cerebral circulation with many serious consequences.
One of the listed complications can lead to the death of the infected. Timely treatment of cholera allows this to avoid.
Diagnosis of the disease

In the diagnosis of cholera, an important point is the clarification of those places where a person could catch this disease-to conduct certain sanitary and epidemiological measures and prevent the outbreak of the epidemic.
Next, the doctor interviews the patient to clarify the features of diarrhea, various pains. Additionally, tests are carried out - a study of feces for the presence of a pathogen, as well as a study of blood for certain antibodies.
Diagnosis of cholera, taking into account the totality of methods, gives an accurate result and allows you to start effective treatment.
Preventive measures
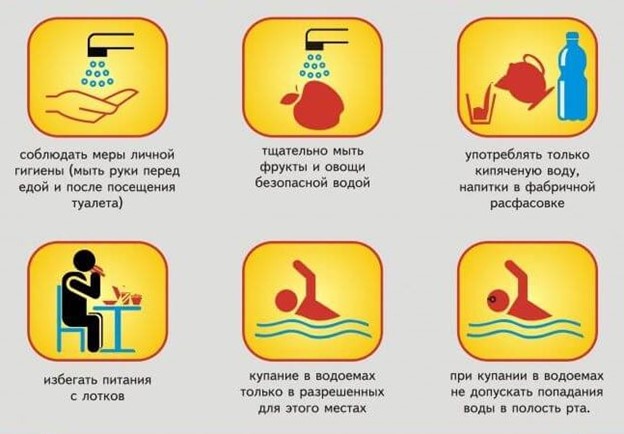
Cholera prevention is as follows:
- Make a vaccine from cholera recommended by WHO. In different countries, the immunization of the population is carried out centrally and strictly controlled. However, it contributes to the development of general immunity - for each particular person, the action of the vaccine weakens over time, therefore other preventive measures are required;
- avoid those countries and regions in which outbreaks of the disease are observed regularly;
- Eat only that food that has passed heat treatment or was well washed with soapy solution;
- use exceptionally clean water from those sources that are intended for this;
- wash your hands regularly;
- Store products in suitable conditions for this - far from the places where insects sit on them.
It is also recommended to monitor the situation in the region, and if cholera outbreaks are detected nearby, it is necessary to enhance control over hygiene, quality of food and water.
Clinical recommendations for the Hollow suggest that people who are attentive to hygiene are least affected and do not visit potentially dangerous places. In the event of a disease, the one who at the first symptoms appears to the infectious disease specialists or calls an ambulance. Also, the described symptoms can be related to other infectious diseases - their timely detection can also save the patient’s life.
Recommendations for all tourists:
- Do not use water for drinking and for household purposes (washing vegetables, fruits, toys and other objects) from random sources;
- Refrain from using ice to cool various drinks;
- Swim in reservoirs allowed for organized relaxation, do not rinse the throat and swallow water, especially on an empty stomach;
- Do not catch crab, mussels, fish and other products of the sea, ocean and other water bodies (lake, river, etc.);
- Do not use raw and insufficiently thermally processed products of the sea, ocean and other water bodies (lake, river, etc.).
- Do not eat foods, fruits and vegetables purchased from street and other random merchants;
- Consume acidified (citric acid) water, juices.
- Wash your hands regularly and thoroughly.
Remember!Risk groups in the Hollow are children, as well as persons suffering from reduced acidity gastritis, undergoing stomach resection, consuming alcohol.
In the presence of infants, especially carefully observe the following preventive measures:
- Before feeding the child, wash his hands thoroughly and treat the chest with clean water (bottled, boiled);
- Do not wash your chest with water from the sea, ocean, rivers, lakes where you rest (bathe, etc.);
- Dilute mixtures for feeding only boiled water;
- Wash dishes in boiled water, store in bags inaccessible to other children;
- If the child appears in the child, immediately consult a medical worker;
- In no case do not self -medicate;
- Wash children's toys daily with soap and soap.
!!! If the mother has symptoms of diarrhea, these measures must be observed when breastfeeding.
When the first symptoms of diarrhea (diarrhea) appear:
- Call the phone indicated in the insurance medical certificate;
- Call the medical officer to the hotel, informing him of the symptoms of the disease;
- Do not self -medicate!




























