Slovekova A.V.
Diabetes mellitus is one of the most powerful risk factors for the development of cardiovascular diseases. In 50% of patients with type 1 diabetes and 80% of people with type 2 diabetes, early disability and premature death are recorded due to cardiovascular complications.
People with diabetes are often at risk of strokes, heart attacks and high blood pressure. Problems with vessels in the limbs are also a frequent complication in diabetes. Moreover, the development of complications can take place asymptomatic for several years.
It is erroneous the opinion that heart disease develops in adulthood and old age. With diabetes, cardiovascular diseases can occur up to 30 years.
Why is diabetes the risk of cardiovascular disease causes?
-In the connection with the increased blood sugar in diabetes, blood vessels constantly suffer -first small capillaries, and then large arteries. It is vascular less flexible, their permeability decreases, and they can no longer fully perform the functions of the nutrition of tissues and organs (in particular, the heart muscle). As a result of vascular violations, the general state of the cardiovascular system is cooked. People who suffer from diabetes mellitus in combination with an excess body mass or obesity, with a constantly increased level of blood glucose, smoking, allowing errors in the diet, with high blood pressure, an increased blood cholesterol and impaired blood coagulation, are more of a higher risk of cardiovascular complications.
Angiopathy is vascular disorders in diabetes, which are characterized by functional disorders in capillaries and arteries caused by changes in the composition of the blood. Angiopathy is an almost mandatory consequence of a constantly increased sugar level.
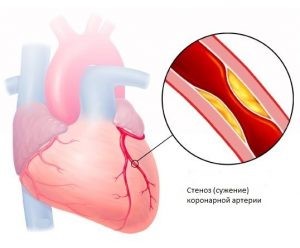 The most common complication in diabetes is coronary heart disease (coronary heart disease), which is caused by narrowing or blocking the blood vessels of the heart. The sergeal muscle (myocardial) experiences oxygen starvation. With prolonged course of diabetes and prolonged oxygen deficiency, ischemia of the heart muscle develops. Authesis of patients with diabetes. This pathology occurs 2 times more often in women than in men.
The most common complication in diabetes is coronary heart disease (coronary heart disease), which is caused by narrowing or blocking the blood vessels of the heart. The sergeal muscle (myocardial) experiences oxygen starvation. With prolonged course of diabetes and prolonged oxygen deficiency, ischemia of the heart muscle develops. Authesis of patients with diabetes. This pathology occurs 2 times more often in women than in men.
The manifestations of heart disease can be:
Angina pectoris is pressing or squeezing the pain behind the sternum or in the heart area, radiating under the left shoulder blade, into the left hand or lower jaw. It occurs, as a rule, with physical activity or excessive emotional excitement. It can take place at rest or when taking nitroglycerin. For time, bouts can increase, the disease flows into the chronic stage.
Myocardial infarction (when the heart muscle is not enough blood supply, there may be a threat of the death of cells-nicrosis of a part of the myocardium or rhythm disturbance). According to studies, people with diabetes are at 40-50% are at risk of heart attack. In the presence of diabetes, a heart attack can prove itself: sharp general insufficiency; unreasonable vomiting; nausea; a violation of the heartbeat; edema of lung tissues; severe pains in the chest and areas of the heart, having compressive or pressing in nature; Pain, giving in the neck, jaw, lower shoulder, shoulder blade or arm, which do not pass after a pill of nitroglycerin.
The course of heart attack in patients with diabetes has the following features:
- The appearance of extensive heart attack;
- Thromboembolic complications;
- Risk of repeated cases;
- A large percentage of death;
- Absence or weak severity of symptoms
Complications of heart disease are heart failure, which is manifested by poor tolerance of physical exertion, general weakness, shortness of breath, edema. In patients with diabetes, complications develop much earlier than in all other risk groups. The danger of complications is that at the initial stage they most often proceed asymptomatic, which complicates the resolution of a timely diagnosis. That's why the timely observation of the cardiologist is so necessary.
Stroke for diabetes.
According to some reports of medical statistics, the probability of a stroke in diabetes mellitus is 2.5 times higher than those who do not suffer from diabetes.
Transient (short-term) cerebrovascular disorder or stroke (the death of a part of the brain cells due to a lack of oxygen) occurs when atherosclerotic plaques damage to the vessels of the brain.
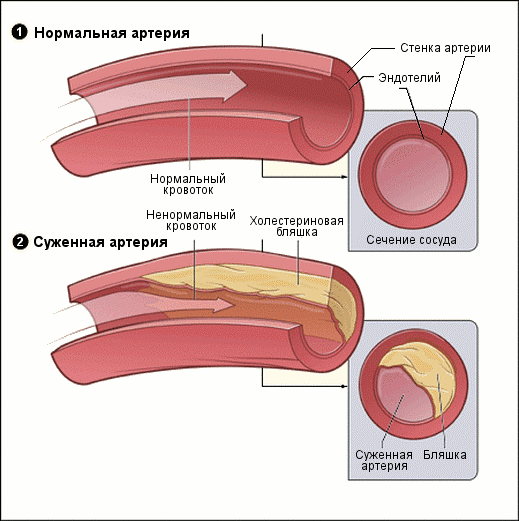
An increase in blood sugar can greatly complicate the stroke. Many doctors noted that with hyperglycemia a section of the brain, affected by a stroke, increased. Only a doctor can establish an accurate diagnosis.
Pay attention to the following symptoms:
Unreasonable pain in the head, weakness, numbness of the extremities (only on the right or left) or the entire half of the body, in one of the eyes the vision, misunderstanding of what is happening, the conversations of others, difficulty or the impossibility of speech, the addition of one or more symptoms of the loss of orientation, balance, and the fall are completely impaired.
The main feature is that the manifestations of a stroke arise sharply, unexpectedly. You need to respond unequivocally: an ambulance.
With damage to the vessels of the legs in diabetes mellitus, pain in the calf muscles when walking, which gradually subside at rest.
Especially often, damage to the vessels of the legs is found in smokers.
Arterial hypertension.
With diabetes, the measurement of pressure is the same vital procedure as constant control of glucose levels. Patients with diabetes suffering from high pressure are highly risk of developing atherosclerosis, which in turn provokes strokes, heart attacks of other serious complications. With diabetes 1 and 2, the causes of hypertension are different. With type 1 diabetes, high pressure develops as a result of kidney damage (diabetic nephropathy). Arterial hypertension with type 2 diabetes develops even earlier than metabolic disorders.
Factors that increase the risk of arterial hypertension in diabetes are:
- Elderly age;
- Deficiency of some trace elements in the body (for example, magnesium);
- Constant psychological and emotional stress;
- Obesity or overweight;
- Concomitant endocrine pathology - diseases of the thyroid gland, adrenal glands;
- Night apnea (lack of breathing during sleep, accompanied by snoring);
- Narrowing of large arteries as a result of atherosclerosis.
Prevention of cardiovascular diseases.
With diabetes mellitus, in order to prevent cardiovascular diseases, careful body weight, daily physical exercises, and abandoning smoking and alcohol are necessary. It is necessary to maintain three main indicators:
- the level of glycated hemoglobin (must correspond to an individual goal);
- blood pressure (less = 140/80 mm. RT. Art.)
- The level of low-density lipoproteins (less than 2.5 mmol/l or 1.8 mmol/l, depending on the risk of developing adverse cardiovascular events).




























