 Ospop monkeys(MPOX("Empox ") - a viral disease common to humans and animals.
Ospop monkeys(MPOX("Empox ") - a viral disease common to humans and animals.
The main tank of the virus in nature is currently Gambian rats, African squirrels, African Sonya.
According to the World Health Organization (hereinafter referred to as WHO), from May 13, 2022 in member states that are not endemic in the Osppege of monkeys, cases of disease among the population are recorded.
On July 23, 2022, the WHO declared the spread of the virus emergency in the field of public healthcare, which is of international significance, May 11, 2023Emergency situationVworldByMPOX disease canceledIn connection with a decrease in the incidence.
More than 90 thousand cases of monkeys were revealed in 116 countries of the world since January 2022.
 Based on the currently available, cases of the disease were identified mainly among men who have sexual contacts with men (MSM), who sought medical help in the primary health care and sexual health clinic.
Based on the currently available, cases of the disease were identified mainly among men who have sexual contacts with men (MSM), who sought medical help in the primary health care and sexual health clinic.
Most cases are registered in the European region, as well as in the countries of the American continent, eastern Mediterranean and the western part of the Pacific Ocean. The infection has received the most widespread in the USA, Brazil, Spain, Portugal, France, Columbia, Mexico, Great Britain, Peru, Germany and China. In January 2024, two cases of Ospa Monkeys were detected in St. Petersburg (Russian Federation) in men who returned from a tourist trip to Hong Kong.
Sporadic flashes Ospes of monkeys registeredAlsoIn endemicfor this diseasecountries(Cameroon, the Central African Republic, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Gabon, Gan, Cot-D'Ivoire, Liberia, Nigeria, the Republic of Congo, Sierra Leone, Benin and Southern Sudan).
Ways and transmission factors.In most cases, infection occurs as a result of close contact with biological fluids (for example, blood), damage to the skin and mucous membranes of a sick person, including during sexual contacts, as well as in tactile contact with infected animals, in contact with infected environmental objects (household items: bedding, personal hygiene towel and more). One of the possible risk factors is the use of infected animals without proper heat treatment. Airogenic infection mechanism is not excluded.
 The period from the moment of infection to the appearance of the first signs of the disease is usually from 6 to 13 days, but can vary from 5 to 21 days.
The period from the moment of infection to the appearance of the first signs of the disease is usually from 6 to 13 days, but can vary from 5 to 21 days.
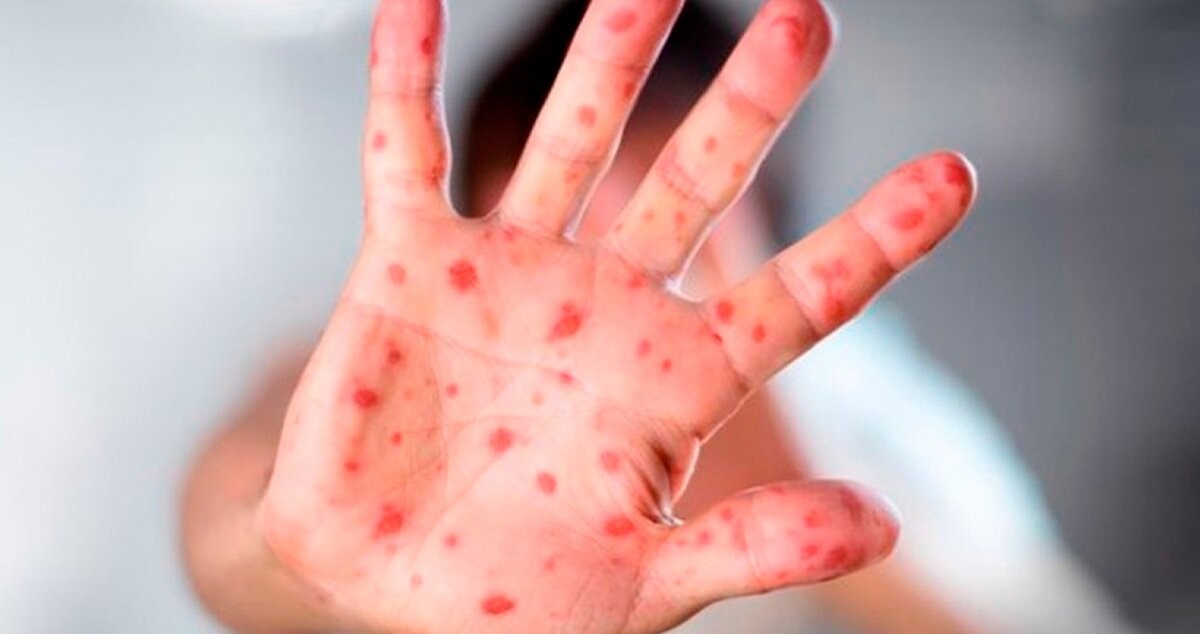
Symptoms of the disease.The disease is characterized by fever, weakness, severe headache, an increase in lymph nodes, muscle pains, a characteristic rash. An increase in lymph nodes is a distinctive feature of monkeys smallpox in comparison with other diseases that can initially seem similar (chickenpox, measles, simple herpes, bacterial skin infections and others). The skin rash usually manifests itself within 1-3 days after the appearance of the fever. The rash in most cases is localized on the face, as well as the palms of the arms and soles of the legs. The mucous membranes of the oral cavity, genitals, conjunctiva and cornea are also affected. The rash develops sequentially from the primary lesions with a flat base to bubbles/bubbles filled with transparent or yellowish liquid. The rash is allowed with the formation of crusts that dry and fall off. The number of skin lesions varies from several pieces to several thousand. In severe cases, damage can be drained.
Symptoms of the disease are preserved for 2-3 weeks. Severe cases of the disease in endemic countries are more often observed among children and are associated with the degree of impact of the virus, the patient's health and the presence of complications.
Mortality varies from 1 to 10%.
Personal prevention measuresThey include the exclusion of close physical contact with a person who has symptoms that do not exclude monkeys OSPU. It is also extremely important to avoid intimate or sexual contacts with someone with localized anogental rash and/or lesions in the mouth. It is necessary to observe respiratory etiquette and hygiene of the hands (washing with water and soap and (or) the use of antiseptic products for processing the skin of the hands).
Travelers when visiting countries, endemic monkeys in smallpox should avoid contacts with animals that can be infected with the pathogen of this disease (rodents, marsupials), refrain from eating meat of wild animals.
In contacts with people who have arrived from countries where cases of disease are recorded, or by persons who have symptoms who do not exclude monkeys OSPU, it is necessary to observe personal prevention measures - use respiratory protection products and observe hand hygiene.
When symptoms appear that do not exclude the OSPU of the monkeys, including during the trip or within 21 days from the date of return, you should immediately seek medical help and inform the medical worker about the facts:
- visits to countries (both endemic and non -endemic), in which cases of monkeys are recorded;
- contact with a person having symptoms that do not exclude the OSPU of the monkeys, or contact with a person with a confirmed diagnosis of the disease, as well as with objects contaminated with biological fluids of such persons;
- Contact, when visiting foreign countries, with a dead or living wild animal or exotic pets, or the use of foods received from such animals.




























