Pain in the chest, which occurs at load and subsides alone, can be caused by angina pectoris. Pathology indicates insufficient blood supply to the heart. If you suspect angina pectoris, you need to consult a doctor as soon as possible and start treatment.
Angina pectoris (breast toad)-This is a pressing or painful pain in the heart, which develops due to insufficient oxygen intake to the heart muscle.
The term "though" is the old name for angina pectoris, which was used in official medical documents before the beginning of the last century. Its origin is definitely unknown: some sources claim that it appeared due to a temporary change in the complexion of the face to gray-green, like amphibians. Others are the reason for the sensations: during an attack of angina pectoris on the chest, it seems to sit a huge toad, interfering with breathing.
The syndrome can develop against a background of stress or sports loads, that is, in situations where the heart needs more oxygen. As a rule, the attack lasts no more than 15 minutes, and then the pain leaves.
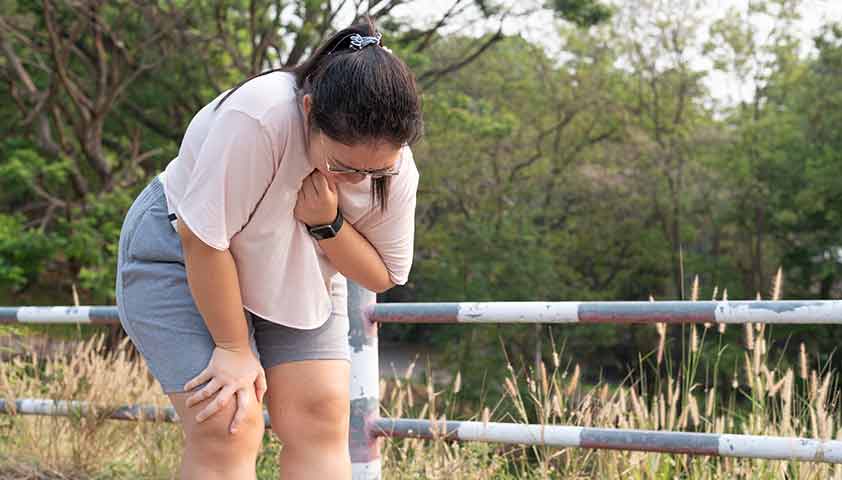

With angina pectoris, it is difficult for a person to continue what he did. During an attack, there is a need to slow down a step, stop or lie down
The peculiarity of the angina pectoris is that the pain almost always appears against the background of the load (physical or emotional) and is at rest.
Angina pectoris is one of the manifestations of coronary heart disease, pathology in which the blood supply to the heart is not enough to ensure its function.
Causes of angina pectoris
Angina pectoris develops due to the gradual narrowing of the vessels that feed the heart muscle. Blood circulation worsens, and the heart receives not enough oxygen. In a calm state, the power deficit can be invisible. But with an increase in the load, for example, during sports or with fast walking, it requires more oxygen for normal heart function and angina pectoris develops.
Vascular narrowing can be caused by violations such as atherosclerosis or vascular spasm.
Atherosclerosis- accumulation of cholesterol deposits on the walls of arteries, which leads to chronic narrowing of the arteries and deterioration of blood circulation.
Atherosclerosis development factors:
- increased content of racescholesterol- a fat -like substance that the body uses for the construction of cell membranes, the synthesis of gall acids, the production of hormones andvitamin D;
- Microtrauma of the inner shell of blood vessels caused by an increased level of glucose of worship or chronic inflammation.
With a combination of these factors, the walls of the vessels gradually begin to grow cholesterol deposits and the cross -country ability of the vessels is reduced.
Vascular spasm- narrowing of the vessels under the influence of prolonged stress, against the background of overwork, hypothermia, fluctuations in atmospheric pressure, smoking or abuse of alcohol. In more rare cases, blood vessels can cause congenital and genetic disorders, an overdose of vasoconstrictor drugs and some drugs.
This type of angina pectoris develops outside the physical activity and can even occur in a dream.
Such a variety of angina pectoris is called vasospastic, or angina pectoris of Princess. Pathology received its name by the name of a doctor who first described it.
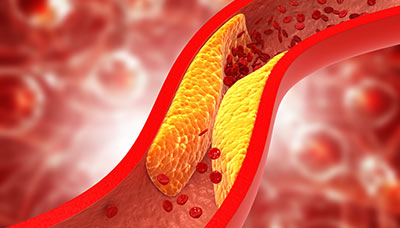
In 95% of cases, the cause of angina pectoris becomes atherosclerosis-narrowing of the lumen of blood vessels due to the formation of cholesterol plaques
There are a number of physiological and behavioral factors in which the risk of angina pectoris increases.
Risk factors for angina pectoris:
- increased level of cholesterol of the ramps;
- Arterial hypertension(increased pressure);
- diabetes(increased blood glucose);
- violation of blood coagulation;
- long infectious diseases;
- Chronic kidney diseases;
- male gender;
- age older than 50 years;
- a hereditary predisposition to the appropriations of blood vessels;
- increased stress;
- obesity;
- alcohol abuse;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- irrational nutrition;
- hypothermia;
- Treatment with some drugs (in the Union of Migraine).
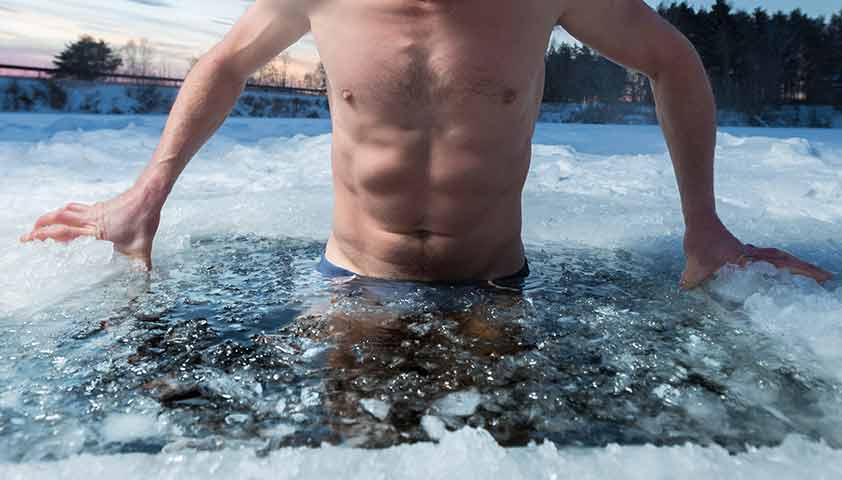

Hypothermia can provoke angina pectoris against the background of vascular spasm
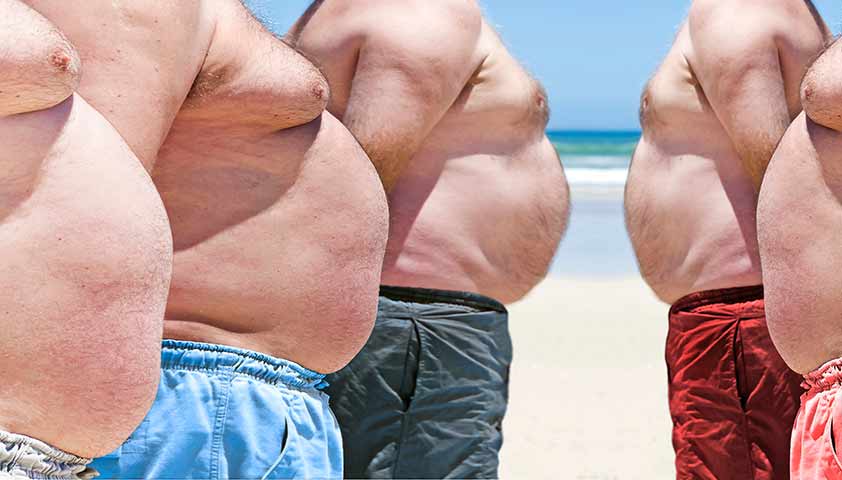

In people's overweight people have to work more to supply the body with oxygen
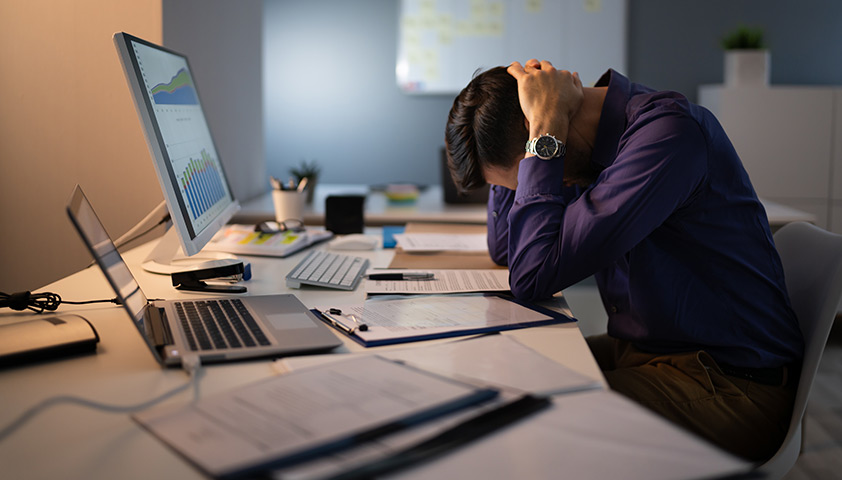

With stress, the arteries narrow, and the lack of oxygen becomes more pronounced
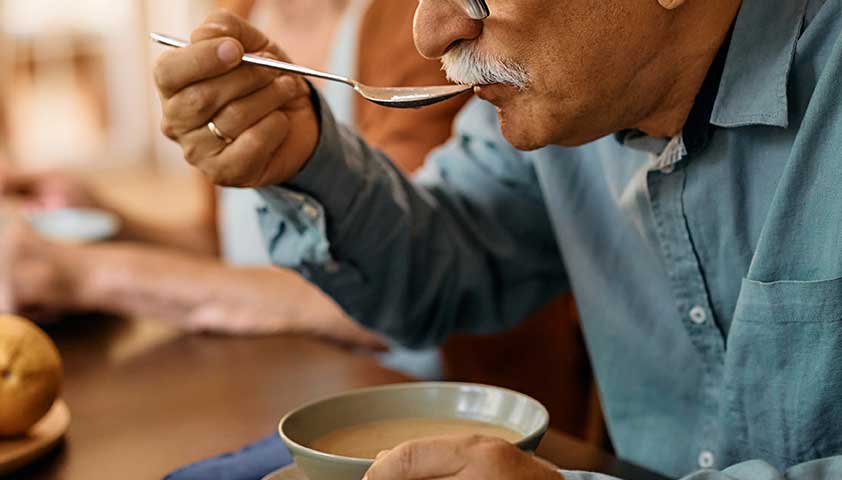

Pain can occur even against the background of unobvious loads, for example, when eating
Symptoms of angina pectoris
Pain in the chest can speak of many pathologies - from circulatory disorders to heart to heartburn or pinching of the nerve. However, pain in angina pectoris has a number of specific symptoms, therefore, as a rule, it is not difficult to distinguish from pain caused by other causes.
What can be attributed to characteristic pains with angina pectoris
A classic attack of angina pectoris has a set of characteristic features.
Signs of angina pectoris:
- Pressure or slander pain of vaguades occurs against the background of physical activity or experiences;
- pain gives handle, neck, jaw, shoulder or spatula;
- The pain makes you stop and the spirit;
- The attack passes in the afternoon and against the background of the intake of nitroglycerin;
- The duration of the attack usually does not fail for 15 minutes.
As a rule, the pain develops gradually and increases if the tension does not slow down. For example, not to slow down a step or not to leave the room where people argue loudly.
Sometimes pain in angina pectoris subsides with an ongoing load, when the heart adapts to a new rhythm. This phenomenon is called "warm -up syndrome."
In some people, angina pectoris can have a lubricated course - in this case, the disease is manifested only by one or two of these signs.
Instead of pain, angina pectoris can manifest itself with a feelingburning, severity or bursting in the chest area
There are a number of additional symptoms that can accompany the angina pectoris.
Other symptoms of angina pectoris:
- dizziness,
- increased fatigue,
- nausea,
- dyspnea,
- increased sweating.
Pain for angina pectoris is compressive or pressing. Short -term stitching, cutting or pulsating point pain does not apply to angina pectoris.
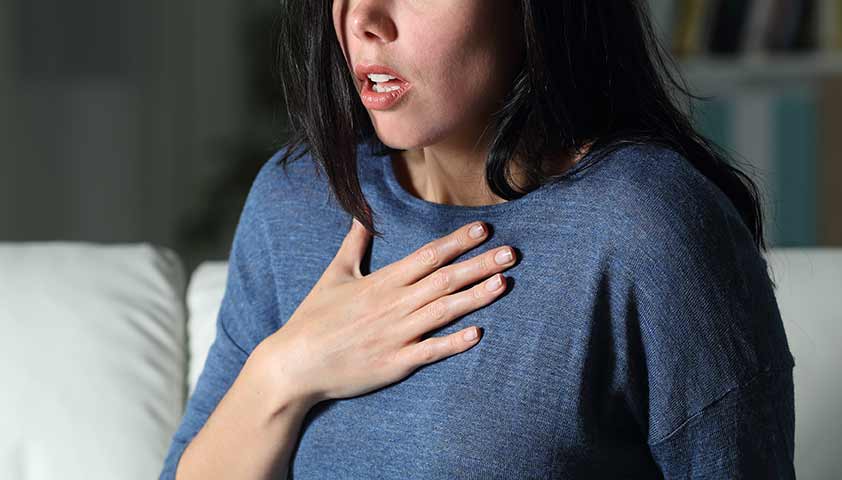

For angina pectoris, the pain that is enhanced by inhalation or palpation is enhanced
Without treatment, angina pectoris progresses. Over time, attacks arise even with a slight load: a person delivers slow walking or simple household chores.
In what cases should you see a doctor
In case of suspicion of angina pectoris - if the attack has developed for the first time - you need to consult a doctor as soon as possible. He will conduct an examination, identify the cause and prescribe treatment.
Patients who are already observed by a cardiologist about angina pectoris need to call an ambulance if the nature of the pain has changed. For example, the attack lasts longer or the pain syndrome is more pronounced than usual.
An unusually painful or prolonged attack of angina pectoris can talk about the development of dangerous forms of heart ischemia.
What to do in the case of an attack of angina pectoris or myocardial infarction
Long -term (more than 30 minutes) circulatory disorders in the heart leads to dystrophy or death of tissues. Therefore, if the chest pain appeared for the first time and does not pass within a few minutes against the background of the rest, you need to call an ambulance.
Actions in anticipation of a doctor:
- reduce the Cinimum of the physical and emotional stress;
- Open the window;
- take a convenient position;
- Remove or unfasten cramped clothes;
- take a pill of nitroglycerin;
- If the pain is inexistence in 10 minutes, take the aspirin tablet.
Types and stages of angina pectoris
There are three varieties of angina pectoris: stable, unstable, vasospastic. They are distinguished by nature, the nature of the course and the risks of complications.
Stable angina pectoris- The most common variety. As a rule, it is accompanied by a classic set of symptoms (the pain is dull, develops against the background of the load, and subsides at rest). With stable angina pectoris, the signs are always the same: the nature of the pain is the same, and the duration of the attack does not increase. Stable angina pectoris occurs due to the plaque formed on the artery’s nutrition.
Four stages of stable angina pectoris are distinguished. They are determined by the degree of overlap of the artery and severity of the syndrome.
Stages of stable angina:
- 1st stage: a person tolerates the usual loads well (for example, training in the mutual or climbing stairs to a certain floor), but if the load increases, this provokes an attack;
- 2nd stage: symptoms begin to occur nafon of the usual physical activity;
- 3rd stage: physical activity is significantly reduced: pain can develop even with slow walking or on time of the simplest household chores;
- 4th stage: attacks develop in a way, and with a light load-intensify.
Unstable (refractory) angina pectorisIt can arise as a complication stable or suddenly, without any prerequisites. It develops due to the rupture of plaques and the formation of a blood clot. With this variety, angina pectoris does not help rest or nitroglycerin.
Unstable angina pectoris requires immediate medical care.
Vasospastic angina pectoris(it is also called the “angina pectoris of Princess”, or “Variant angina”) - a very rare variety. It is not related to the formation of plaques or blood clots and occurs against the background of a spasm of an artery that feeds the heart. The spasm of the artery can develop under the influence of stress, some drugs or with severe hypothermia. Vasospastic angina is developing outside physical exertion.
Angina pectoris can develop during a quick phase of sleep, when the heart begins to fight more often
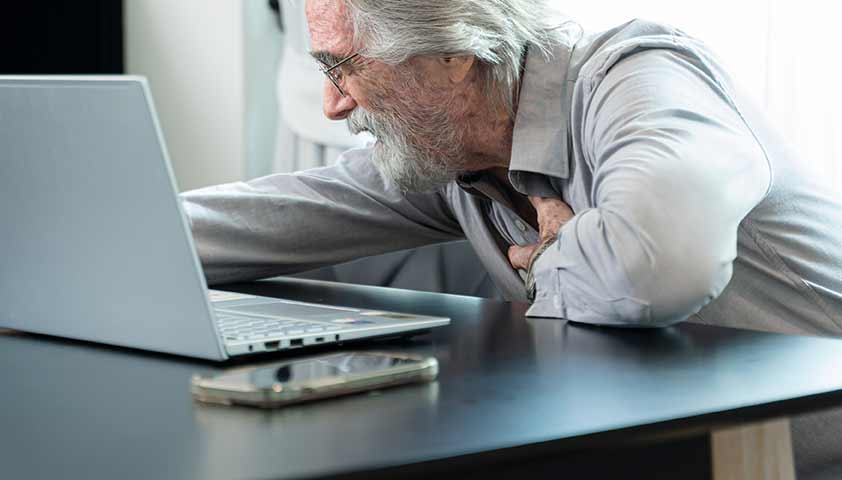

Vasospastic angina is characterized by very strong attacks
The development of symptoms distinguish between typical and atypical angina pectoris. Attypical anginaAll the main symptoms are present: pressing pain occurs against the background of physical activity and subsides during rest, usually within 15 minutes. Atatypical angina pectorisThere may not be any of these signs-for example, the pain does not pass against the background of rest.
Diagnosis of angina pectoris
If you suspect angina pectoris, you need to consult a therapist or cardiologist - a doctor who is responsible for the health of the heart and blood vessels. If necessary, he will direct the patient to other specialized specialists: a neurologist, nephrologist, endocrinologist.
Diagnosis for angina pectoris begins with the collection of complaints. The doctor also learns from the patient whether he suffers from chronic diseases (for example, diabetes or renal failure). An important stage is an analysis of information about diseases in the family. For example, if someone from close relatives suffers from cardiovascular pathologies or diabetes mellitus, the patient obviously has a higher risk of angina pectoris.
Next move to the inspection. The doctor evaluates the patient’s constitution, measures the waist, pressure and pulse-these indicators allow you to make primary conclusions about the state of the cardiovascular system. The cause of breast pain can be pathologies that are not related to disorders of the heart, such as intercostal neuralgia orEsophageal reflux. The doctor conducts a number of tests to exclude them.
Based on the results of the inspection, laboratory and instrumental studies are prescribed.
Laboratory research
First of all, laboratory studies are prescribed to evaluate the quality of fat metabolism. Its violation leads to atherosclerosis - the formation of cholesterol plaques on the walls of arteries.
Instrumental diagnostics
Instrumental diagnostic methods are prescribed to assess the condition of the heart, vessels and organs that are closely related to the work of the cardiovascular system.
The electrocardiogram (ECG), conducted outside the attack, does not diagnose angina pectoris, but allows you to evaluate the functioning of the heart (rhythm disturbances, an increase in departments) and identify the transferred myocardial infarction.
The ECG with load helps to diagnose angina pectoris: the study is carried out during or after the patient has studied on a treadmill or an exercise bike. EchoCG can be carried out according to the same principle, after classes on the simulator. The load of heart research imitates situations in which angina pectoris can develop.
If possible, Holter (daily) monitoring is carried out - the patient is installed for 24 hours and the sensors and the miniature ECG apparatus are installed. The accuracy of the study is due to the fact that a person during the day is engaged in his usual matters and indications are removed in different conditions: at rest, with physical exertion, in a dream.
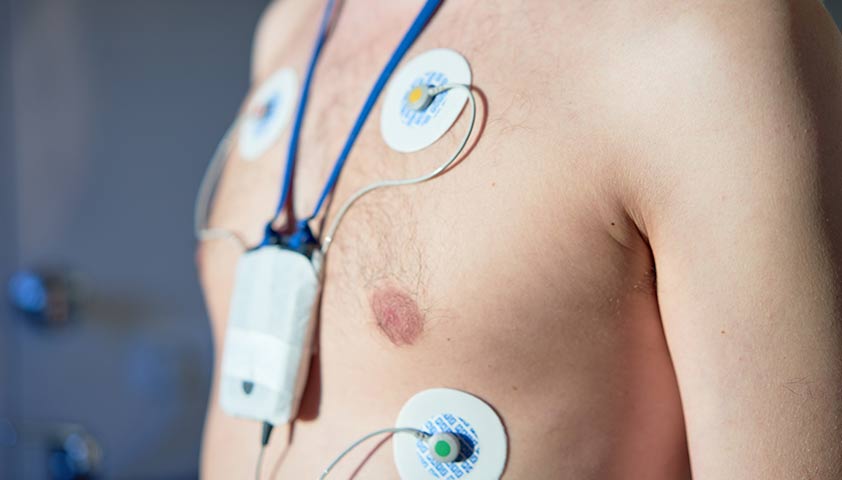
Daily monitoring of ECG allows you to identify the features of the heart at rest and at the load
An ultrasound examination of the heart (echocardiography) is used to evaluate the structure of the organ, to detect changes in its tissues and departments.
Differential diagnosis
Pain behind the sternum can be caused by pathologies that are not associated with the cardiovascular system. For example, esophageal reflux (stomach disease that provokes heartburn) or neurological causes. Also, pain can be caused by a cardiological pathology that is not associated with circulatory disorders, such as inflammation of the heart muscle.
To determine that the symptom is provoked by angina pectoris, they pay attention to a number of characteristic features.
The difference between angina pectoris and other pathologies:
- The pain begins and enhances during physical activity or in situations where the need for the heart in oxygen increases (for example, with severe stress, when the pulse quickens);
- The pain gives to the left hand, neck, jaw or spatula;
- The attack lasts up to 15 minutes;
- The pain takes place at rest or after taking nitroglycerin.
If the pain manifests itself differently (for example, begins at rest, lasts several hours or intensifies with palpation of the chest), then, most likely, it is not caused by angina pectoris.
Diseases that can cause chest pain:
- From the gastrointestinal tract: gastroesophageal reflux, hernial hernia of the diaphragm,peptic ulcer;
- From the lungs: pneumothorax (air accumulation in the lung shell); pneumonia, pulmonary embolism (blockage of the pulmonary artery), pleurisy (inflammation of the thin shell of the lungs);
- From the musculoskeletal system: Riber injuries, muscle spasm;
- From the psyche: panic attacks, anxiety.
Treatment of angina pectoris
Despite the fact that the attacks of angina pectoris pass independently or after taking the medicine, the pathology cannot be ignored. The processes that cause angina pectoris (as a rule, this is atherosclerosis-narrowing of arteries due to cholesterol deposits), over time, progress and can lead to life-threatening complications.
The main goals of the treatment of angina pectoris:
- reduce the frequency and intensity of pain attacks;
- Slow down atherosclerotic changes in blood vessels;
- reduce the risk of cardiovascular complications: acute coronary syndrome,myocardial infarction, heart failure.
For the treatment of angina pectoris, non -drug, medicinal and surgical methods are used.
Non -drug treatment
The condition of the cardiovascular system has a great influence of lifestyle. On how a person eats, sleeps and moves, largely depends on his physical form, the state of blood vessels and metabolic processes. Correction of lifestyle involves a revision of nutrition, restoration of normal physical activity, establishing sleep and work with emotional stress.

It is important even to those patients who undergo medical or surgical treatment to reconsider a lifestyle
Working with food is aimed at normalizing fat metabolism, strengthening blood vessels and maintaining a healthy weight.
For vascular diseases, it is recommended to eat more fresh vegetables and fruits (recommended norm - 300-400 g per day). They contribute to the acceleration of metabolism and contain trace elements necessary for the health of the heart and blood vessels (calcium, potassium).
Fish (at least twice a week), nuts, vegetable oils contain useful fats and are also necessary to strengthen blood vessels.
Magnesium dairy products contain magnesium - this macro element stabilizes the work of the heart.
With increased cholesterol, it is better to reduce the use of animal fats (including excluding fatty meat).
It is recommended to reduce the use of products that contribute to weight gain (sugar, baking).

To reduce the risk of atherosclerosis, it is recommended to choose dairy products with the smallest oily

3-4 medium fruits or vegetables per day - the recommended norm of plant fiber for heart health
Physical activity should be regular and unexplored. Regular charging in the morning, daily walks with a gradual increase in the number of steps per day and the pace of walking help to gently train the heart and blood vessels so that they are in good shape. Information about the recommended time of classes is different. Some experts believe that a healthy minimum for cardio loads is 30–40 minutes three times a week. Others recommend walking or doing at least half an hour a day.

For a walk to bring maximum benefits for blood vessels, it is recommended to go without stops for 30-40 minutes
Refusal of smoking and alcohol is an important step in the treatment of cardiovascular pathologies. These dependencies provoke spasms, worsen the quality of vascular tissue, accelerate the growth of atherosclerotic plaques and make the blood thicker and more viscous, complicating the functioning of the heart and increasing the risk of dangerous vascular complications.
Drug treatment
Medication treatment of angina pectoris is aimed at relieving pain, prevention of new attacks in the future, slowing down the development of vascular pathologies that provoke it, as well as to reduce the likelihood of developing hazardous cardiovascular complications.
To relieve an acute symptom of angina pectoris, use drugs that reduce the need for the heart muscle in oxygen or increase the throughput of blood vessels. The action of the first group of drugs is to slow down the pulse, and the action of the second in the expansion of the vessels due to the relaxation of the smooth muscles.
Out of seizure, therapy is aimed at normalizing the tone of arteries that feed the heart.
Along with medicines, drugs that reduce blood cholesterol and slowing off the development of atherosclerosis are used to stop and prevent angina bouts. This measure can significantly reduce the likelihood of dangerous cardiovascular complications.
Drug therapy is aimed at reducing cholesterol, normalization of blood pressure and reducing blood viscosity (this is necessary if there is a risk of thrombosis). Cardioprotectors (drugs to protect the heart muscle) can also be prescribed, but the benefits of their use requires further research.
Surgical treatment
If drug treatment does not help and the risk of cardiovascular complications is too high, the doctor may decide on surgical treatment-vascular revascularization. This is an operation to resume blood supply in arteries that feed the heart muscle.
Revascularization methods of arteries:
- Boundry angioplasty and stenting of coronary arteries,
- Coronar shunting.
Stenting (expansion of the vessel section using a frame from a metal mesh) or shunting (bypassing the affected part of the aorta using a vascular transplant - shunt).
Stntting allows you to establish blood flow in the existing artery. It is carried out in combination with balloon angioplasty.
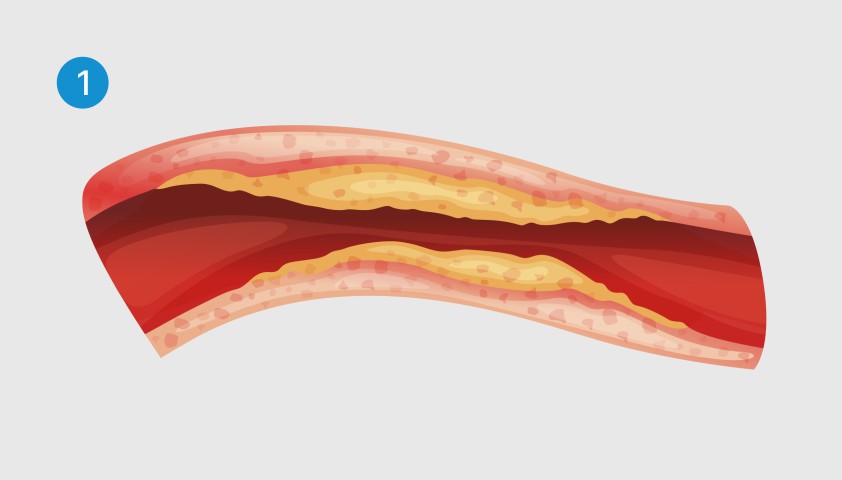
Cholesterol deposits block the blood flow into the arteries
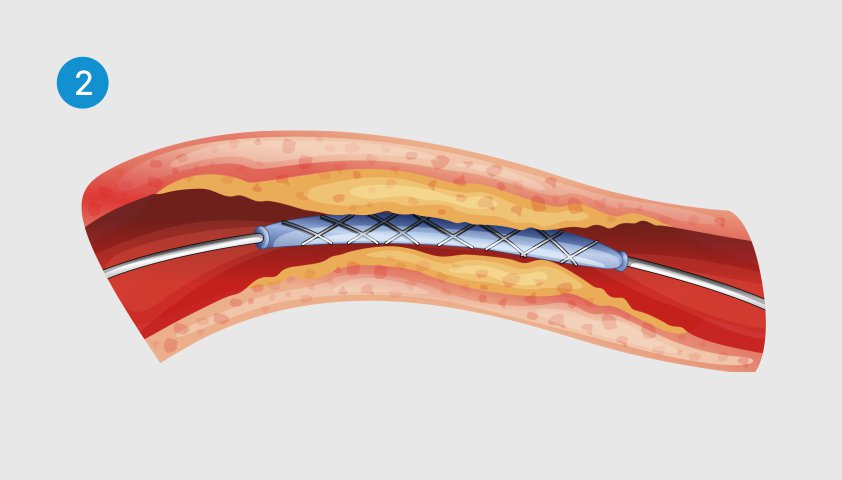
A stent is introduced into the artery - a thin metal tube with a cylinder catheter inside
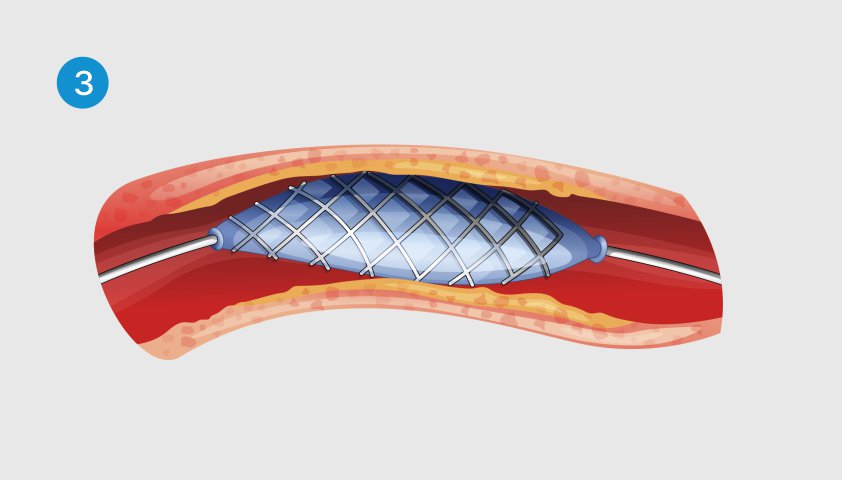
The cylinder is inflated, the stent straightens and expands the walls of the vessel
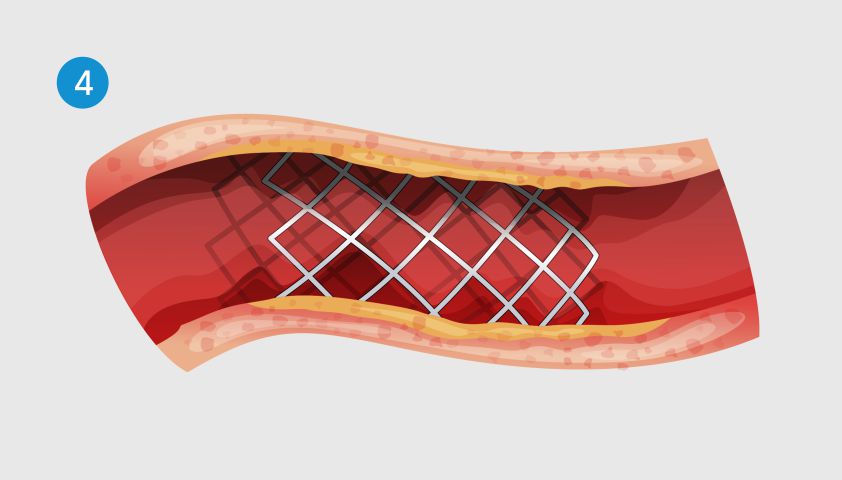
The cylinder is extracted, and the stent remains inside the artery, supporting its walls
Shunting is carried out if the blood flow in the damaged artery is restored. To do this, bypassing the clogged area of the artery, an additional vessel is installed, which allows you to establish tissue power. Shunt is formed from the patient’s own vessels (as a rule, this is a small area of the chest or radial artery or vein of the legs).
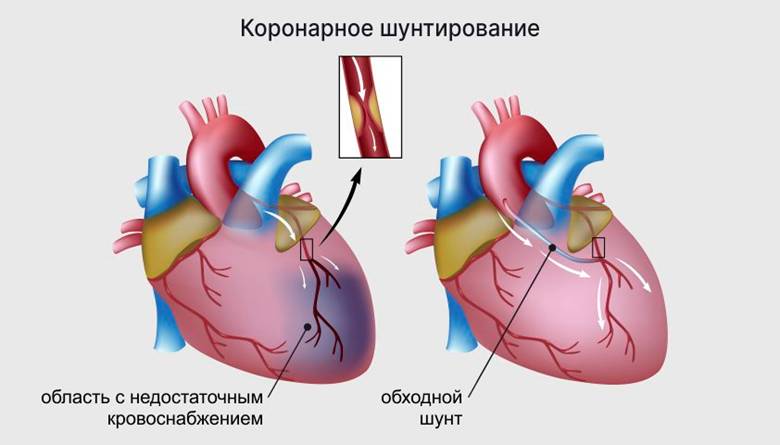
Coronary shunting allows you to lay a bypass for blood flow in a place where the cross -country cross -country
The doctor makes a decision on the treatment method based on their anatomical features of affected arteries, the magnitude of vascular damage, and the general condition of the patient.
Complications of angina pectoris
If you do not treat the disease that caused angina pectoris (in most cases it is atherosclerosis), this can lead to dangerous, including life -threatening consequences. Over time, stable angina pectoris (oxygen starvation occurs only during increased loads) can develop into unstable (oxygen starvation occurs without connection with the load). This is a dangerous condition that can provoke a heart attack - the death of the cells of the heart muscle against the background of insufficient blood supply.
Long -term angina pectoris also contributes to the development of cardiac arrhythmia (impaired heartbeat rhythm) and chronic heart failure (pathology in which the heart cannot distilty the necessary volume of blood).
Forecast
The prognosis of angina pectoris is influenced by many factors: from the lifestyle and the resulting treatment to genetic predisposition, weight, gender and age. For example, the likelihood of developing complications in men is higher than in women, and gradually increases with age.
In people with atherosclerosis, diabetes and chronic kidney diseases, the risk of death from cardiovascular complications exceeds 15%.
If a person is observed with a doctor and receives adequate treatment, the prognosis is favorable.
Prevention
To reduce the risk of undesirable consequences for angina pectoris, it is important to comply with the doctor’s recommendations for treatment and lifestyle.
Measures for the prevention of cardiovascular complications in angina pectoris:
- Timely treatment of the disease causing angina pectoris: even if angina attacks are concerned about the patient occasionally, supporting therapy is necessary, which will avoid dangerous complications;
- lifestyle correction - primarily weight control, physical activity, rejection of bad habits, healthy nutrition;
- Regular visit to a cardiologist or therapist: since most pathologies that cause angina pectoris are progressing over time, patients need observation.
To reduce the risk of cardiovascular complications, annual flu vaccination is recommended for patients with angina pectoris.
What needs to be done so that the angina does not appear
To prevent angina pectoris, you need to take care of the health of the cardiovascular system: maintain a healthy weight, monitor nutrition. Since in most cases, angina pectoris occurs with atherosclerosis (vascular narrowing due to cholesterol deposits), it is recommended to regularly check the blood cholesterol level. The frequency of analyzes is determined by the doctor based on factors such as health status, family history, and the effect of the environment.
Information material was prepared by employees of the cardiology department No. 2.




























