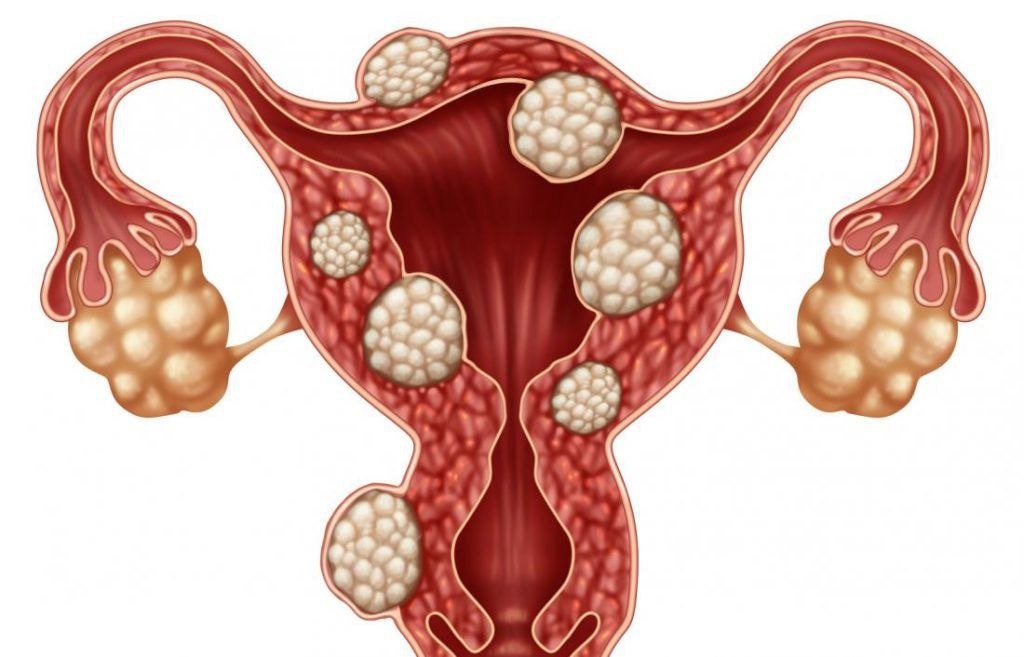
Myoma is the most common benign uterine tumor, it can be found in about 70% of women. In most cases, this pathology proceeds asymptomatic.
Manifestations more often depend on the location of the node and its size.
The most frequent symptoms of myoma:
-Bisy and painful menstruation (characteristic more for nodes located in the cavity and wall of the uterus), which most often leads to a decrease in hemoglobin
-theral pains in the lower abdomen- more often with a violation of the node power (usually with large nodes)
-mind the volume of the abdomen (sometimes the body of the uterus with fibroids can reach up to 20 and even 30 weeks of pregnancy)
- infertility (more often: if the nodes are located in the areas of the uterine mouths and the migration of spermatozoa interferes or submucous and interfere with the implantation of the fetal egg)
-cature and violation of the surrounding organs- bladder, intestines
Diagnostics:
- An annual examination of the doctor of an obstetrician-gynecologist, during which the patient's complaints and bimanual manual examination are assessed
-The pelvic organs -in modern realities, a very affordable and informative method in the diagnosis of a hoax, evaluate their size and location. Today there is a method of an ultrasound of the pelvic organs with 3D reconstruction, which is more informative in terms of diagnosis of the type of submucous node (type 0, type 1, type 2)
-in complex and incomprehensible cases, MRI of the Pilgrief organs is used
-The conservation of hysteroscopy is a highly informative method in the diagnosis of endometrial pathology, including submucous myomatous nodes.
The treatment of myoma is quite difficult, since the exact causes of its occurrence are not clear. Accordingly, there is no single correct method. The choice of the method is determined, as a rule, with complaints (for example, constipation when the rectum is compressed), symptoms (abundant menstruation, anemia) fibroids and women reproductive plans.
With small sizes and asymptomatic course, a dynamic observation is very often enough- examination of the doctor and ultrasound of the OMT once every 6-12 months.
Largely can be divided by treatment methods into 2 large groups: medication and operational.
No drug method will force a myomatous node to disappear. The main task of this method is to reduce symptoms, most often it is abundant menstruation. The main groups of drugs-agonists gonadotropin-rilizig hormones, hormonal spiral "Mirana", selective modulators of progesterone receptors, COC.
Operational methods:
- Mimectomy - removal of the node with laparoscopic or laparotomic access, submucous nodes are preferably removed using hysteroreusectoscopy. These methods allow you to maintain fertility (the ability to give birth in the subsequent)
- Hysterectomy - uterine removal
Embolization of the uterine arteries.